Reported by: Samuel Ernest.
Date: 25th February, 2025.
Lusaka, Zambia.
Zambia has taken a significant step towards sustainable electronic waste (e-waste) management by advancing the implementation of the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) in the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) sector. In a bid to develop a structured regulatory framework, key stakeholders convened at the Second High-Level Breakfast Meeting in Lusaka, hosted by the Communication, Space, and Technology Commission (CSTC) in collaboration with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
The meeting brought together electronics industry leaders, waste management entities, and government regulators to align on Zambia’s transition towards a circular economy for electronic waste. Representing the Minister of Technology and Science, Hon. Felix Chipota Mutati, Director of Communications, Mr. Nkula Mwanza, emphasized the urgent need to establish a functional EPR system that ensures sustainable e-waste management.
The rapid expansion of Zambia’s ICT sector has fueled digital transformation, improved access to information, and enhanced economic opportunities. However, this progress has come with a significant environmental challenge—the accumulation of electronic waste. According to the 2022 National Survey on Access and Usage of ICTs, 44% of respondents reported improper disposal of electronic devices, underscoring the need for a structured waste management system.
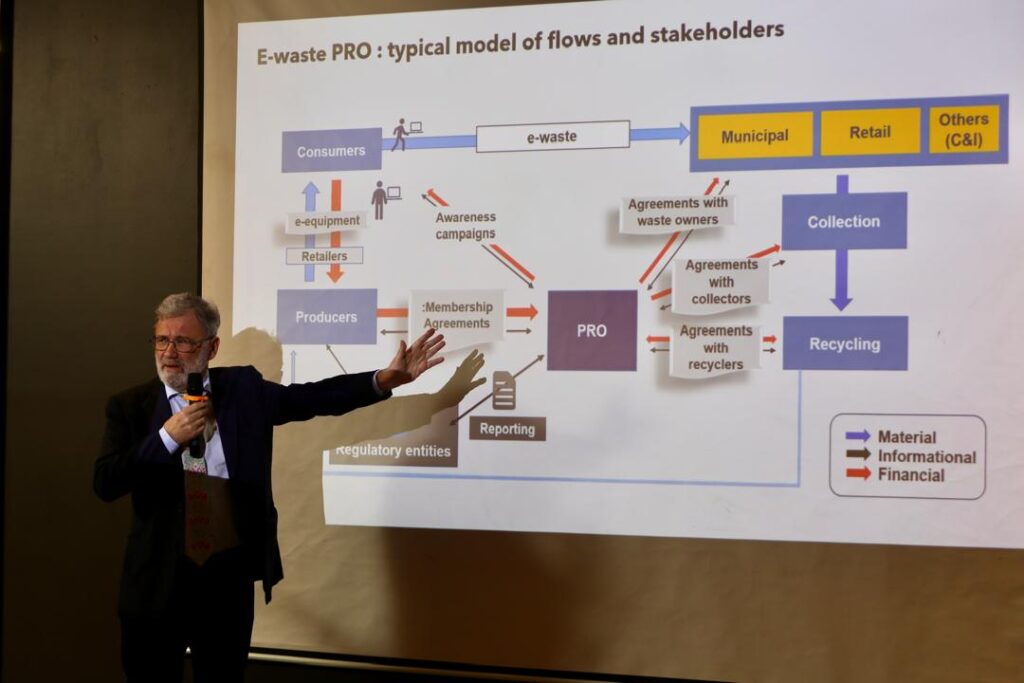
Zambia’s legal framework for environmental protection is rooted in the Environmental Management Act (EMA) No. 12 of 2011, which mandates the implementation of EPR under Article 58 (1). Despite its introduction over a decade ago, this provision has not been enforced, nor have the financial and administrative structures been developed to hold producers—manufacturers, importers, distributors, and resellers—accountable for e-waste management.
To address this gap, Zambia has secured technical assistance from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and financial support from the Communications, Space, and Technology Commission of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. This collaboration aims to build a comprehensive regulatory framework that will facilitate the proper collection, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste.
The EPR implementation strategy is structured around three key pillars:
- Legal Framework Development
Drafting national regulations governing EPR for electronics.
Aligning e-waste policies with technical regulations.
Establishing EPR implementation guidelines for the electronics sector.
- Financial Mechanisms
Conducting a cost analysis of e-waste management.
Proposing a structured EPR fee system for electronics producers.
Engaging industry stakeholders to develop guidelines for compliance.
- Administrative and Digital Integration
Exploring digital services to streamline regulatory enforcement.
Defining stakeholder roles and responsibilities across the EPR system.
Strengthening compliance and enforcement mechanisms.
With these strategic measures, Zambia is laying the groundwork for a sustainable, circular economy in the electronics sector. The implementation of EPR will ensure that producers take full responsibility for the environmental impact of their products, reducing electronic waste and promoting resource efficiency, recycling, and responsible disposal.
As Zambia continues to advance its digital economy, the integration of a robust EPR system will be pivotal in balancing technological growth with environmental sustainability. This initiative marks a critical milestone in the country’s journey towards a cleaner, greener, and more responsible ICT industry.
The Agency.